Coriolis sensors or cheaper thermal anemometers - sometimes with chamber head technology - are often used for exact flow measurement of gases. The thermal anemometers essentially offer the performance range of the Coriolis sensors. The decision for a measuring principle depends on the application of details.
Measurement of gas flow in industrial applications
The precise measurement of gas flow is required in many industrial applications. The use of flow sensors / flow sensors with the following objectives has proven itself here:
- Energy saving / energy efficiency
- Collection of consumption data
- Process quality assurance
- Ensuring the safety of people and devices
- Function monitoring
Suitable technologies for measuring the flow of gases in comparison
Suitable technologies for flow measurement are for these cases
- Coriolis sensors
- Thermal anemometer
Both measuring principles have advantages and disadvantages:
| Coriolis sensors | Thermal anemometers | |
 |
 |
|
| Advantages: |
|
|
| Disadvantages: |
|
|
| Applications: |
|
|
Anemometers work according to the thermal measuring principle.
 |
|
This has many advantages:
- Detection of the smallest currents
- No moving parts - no wear
- Volume flow measurement without any further measured variable
- Extreme measuring range limits
- Long-term stability
- Direction detection
- Easy assembly and quick commissioning
Operating modes of the thermal anemometer
Thermal anemometers can follow two operating modes:
- CCA = Constant Current Anemometer
- CTA = Constant Temperature Anemometer
CTD = Constant Temperature Difference Anemometer. This combines the advantages of the CCA and CTA methods. In this case, a temperature overshoot compared to the environment is conveyed to the sensor and kept at a constant level.
This has the following advantages:
- Good resolution with low flow speeds
- Can measure high flow rates
- Particularly quick response
- High operating temperatures achievable
The chamber head
 |
The chamber head of our flow sensors extends the use of the anemometer. |
Its advantages:
- Pressure-tight up to 16 bar / 40 bar
- Applications in pipes up to D = 2 m
- High measuring range dynamics (0.2 m/s to 220 m/s >1:1000)
- Installation tolerance +/- 3° in flow direction
- Bidirectional measurement possible (2 sensors required)
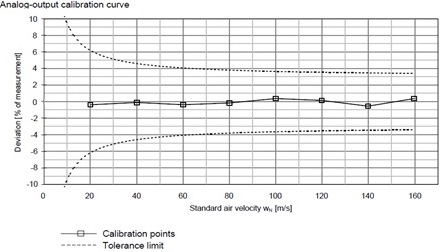
- Precise measurement and reproducibility (see calibration certificate)
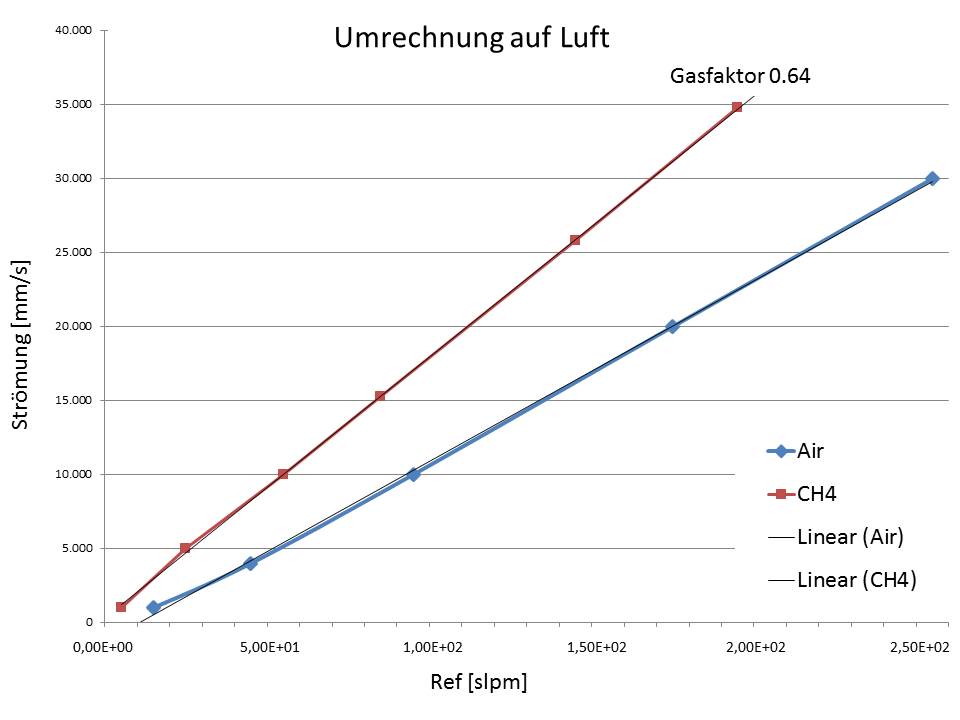
Different gases - is that possible?
By converting to the standard air volume flow, all gases can be measured, but correction factors must be taken into account.
Calibration
 |
Calibration takes place in the wind tunnel up to 220 m / s (in the closed reference tunnel). Optionally, a high-precision comparison with a certificate is created. An ISO calibration certificate, traceable to national standards, is also possible. |
Applications
Our flow meters for gases have already been used and tested in numerous industrial processes:
| Use in compressed air |
|
| Use in all kinds of industrial processes |
|
| Use in cleanrooms |
|
| Use for |
|

