The level in large tanks is very often determined indirectly using pressure sensors (also known as pressure transmitters or pressure transducer). This is a simple and robust method, especially in open containers. Relative pressure sensors are used in open vessels.
A water column with a height (h) of 10 m exerts a pressure of approx. 1 bar on its base (G). The relationship between level and pressure is linear. So a change in pressure of 1 mbar indicates a change in level of 1 cm.
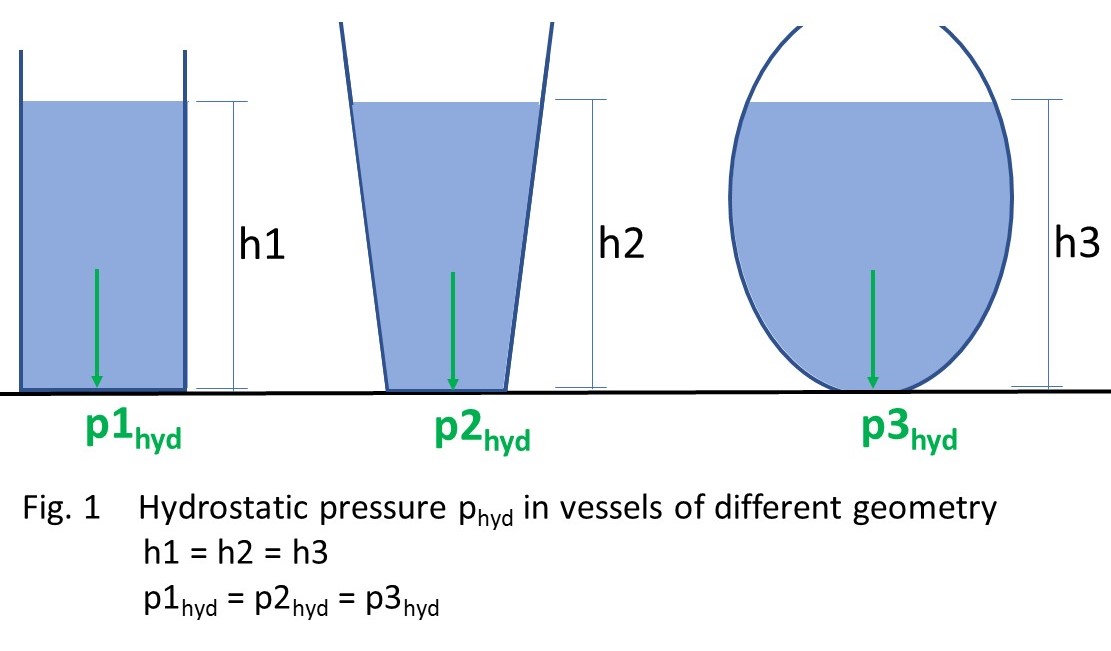
The hydrostatic pressure phyd is independent of the geometry of the vessel.
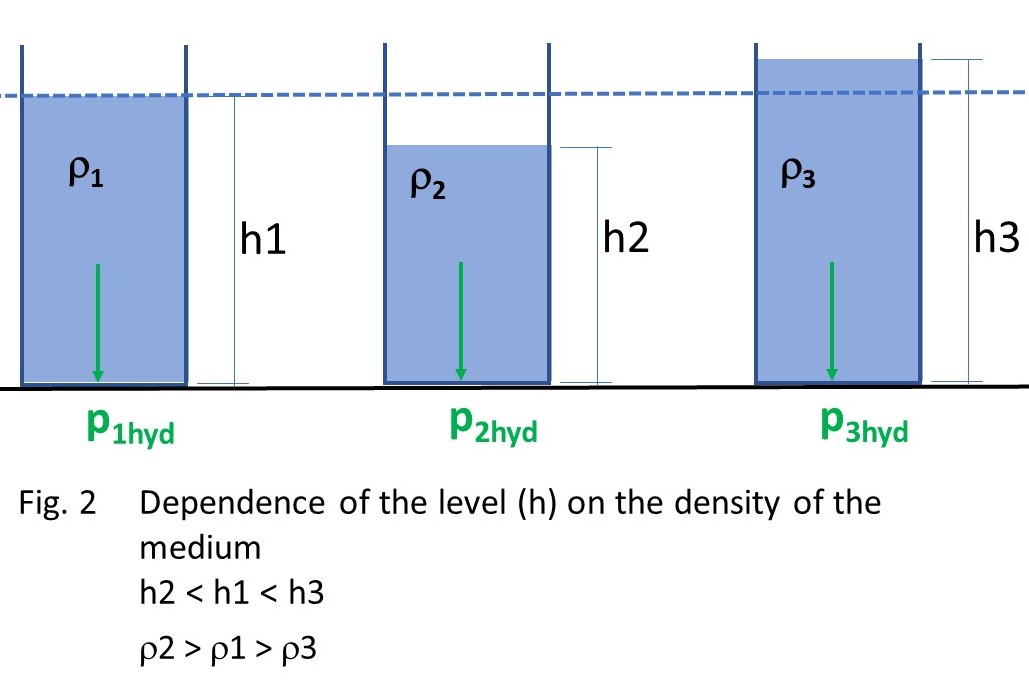
However, the level depends on the density (ρ) of the medium to be measured.
The density (ρ) of water is about 1 g/cm3 (0.998 g/cm3 at 20 °C). Oils have lower densities (approx. 0.8 – 0.9 g/cm3), while 37% hydrochloric acid (approx. 1.2 g/cm3) and solutions containing sugar (60% sucrose approx. 1.3 g/ cm3) have higher densities.
If at the same hydrostatic pressure phyd the levels h2 < h1 < h3, then the media have different densities (ρ2 > ρ1 > ρ3).
The specific density of the medium to be measured must therefore be included in the calculation of the level h:
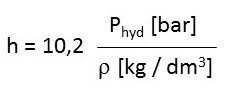
Here, the constant 10.2 corresponds to the reciprocal of the acceleration due to gravity (1/9.81 m/s2).
Attention: The density of the medium depends on the temperature. Unless otherwise stated, density specifications apply to 20 °C.
The use of the 981 pressure sensor (pressure transmitter, pressure transducer) to measure the hydrostatic pressure in open vessels is particularly convenient because it does not have to be attached to the bottom of the vessel. The pressure is measured via a hose that is lowered to the desired measuring point. The use of the hose also prevents the pressure sensor from becoming clogged with small solid components in the medium, e.g. from fruit juices, yeast mixtures, milk, waste water or other suspensions.
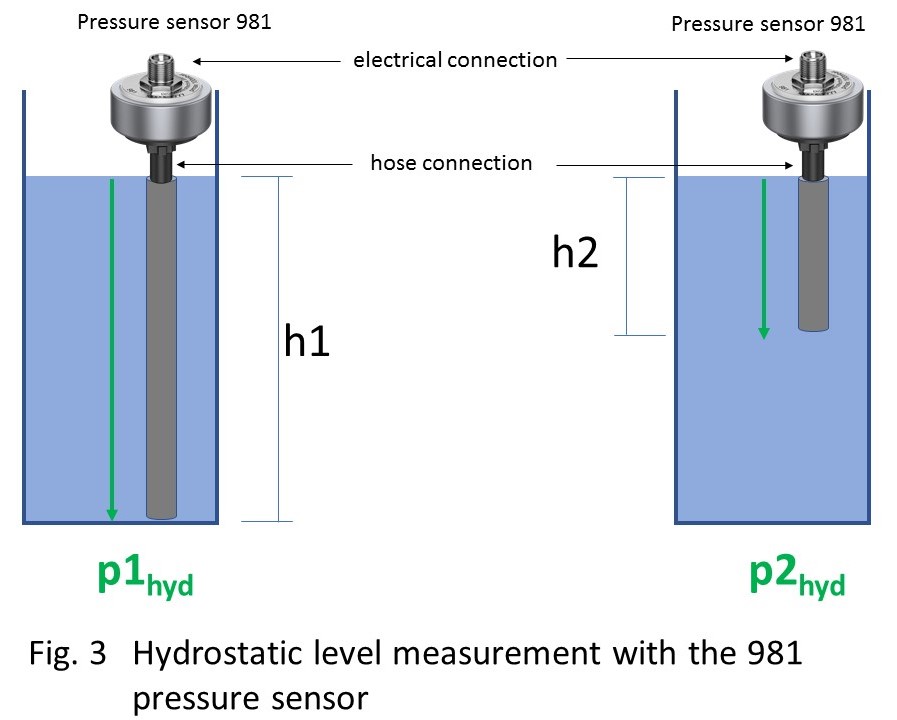
The advantages of hydrostatic level measurement with the pressure sensor 981:
- Measuring device outside the medium, easy installation
- Also suitable for oils and aggressive media
- Independent of agitated surfaces
- Independent of foam formation
- Independent of rapid level changes (response time 500 ms)
- Independent of installations
- Independent of the geometry of the container
- Independent of the conductivity of the medium